- Home
- Know-how
Fidia's know-how
- Hyaluronic Acid (HA), also called hyaluronan, is a high molecular weight polysaccharide, discovered in 1934, by Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer at Columbia University, in the vitreous of bovine eyes.
- The HA molecule is composed of repeating molecular units of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, that form a very long, linear polymer that is completely conserved throughout a large span of the evolutionary tree, indicating a fundamental biological importance.
- Hyaluronic Acid is a major component of the extracellular matrix and can be found in skin, joints, eyes and most other organs and tissues.
- HA is biocompatible and biodegradable molecule and lacks immunogenicity naturally.
- Amongst extracellular matrix molecules, it has unique hygroscopic, rheological and viscoelastic properties. Hyaluronan is one of the most hygroscopic molecules in nature (1 gr of hyaluronic acid can bind up to 3 L of water.)
- Through its complex interactions with matrix components and cells, hyaluronan has multifaceted roles in biology utilizing both its physicochemical and biological properties.
However, these properties are also highly dependent on chain length. HA can reach over 107 Da in molecular mass (HMW-HA), but also exists in multiple smaller forms, referred to as low molecular weight HA (LMW-HA).
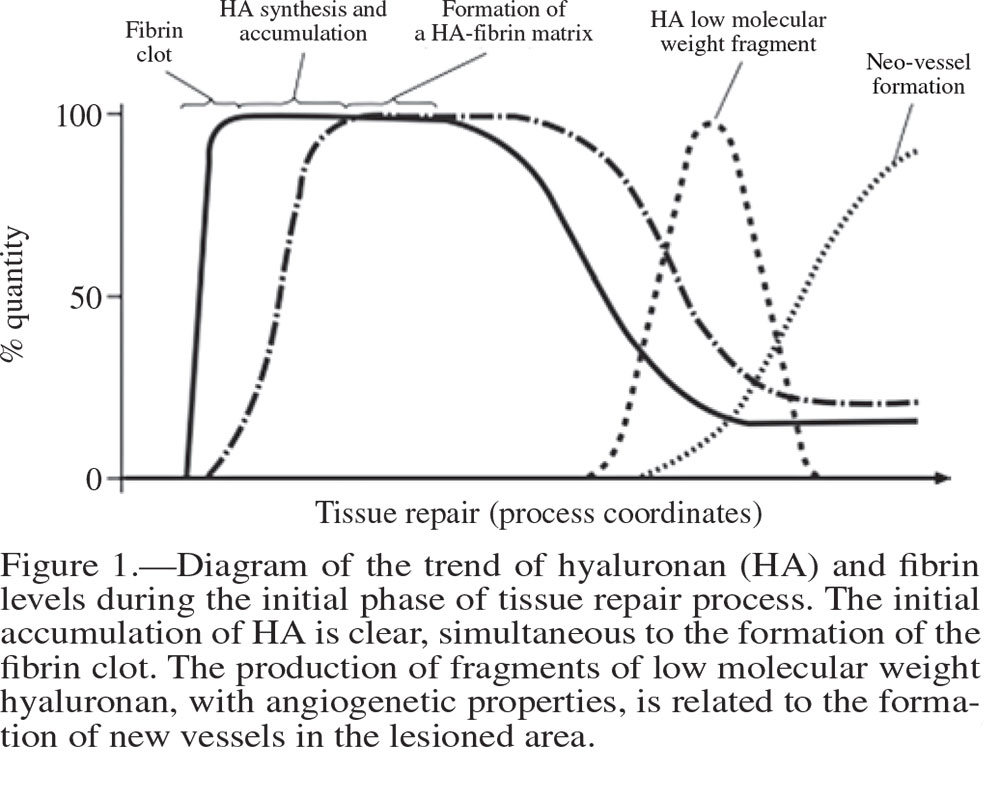
- HA is present through all the steps of wound healing.
- Exogenous HA has been used for decades and is now widely recognized by clinicians and patients as an important agent for tissue repair.
- Its biological properties supporting the clinical application in wound repair have been the subject of several excellent reviews and indeed it is now recognized that its addition
1)increases the migration and proliferation of fibroblasts and the formation of granulation tissue;
2)promotes the organized deposition of collagen fibers by the fibroblasts;
3)promotes the formation of new blood vessels (neo angiogenesis), and
4)favors re-epithelialisation
More specifically, has been demonstrated that topical use of specific fragments between 100 and 300 kDa could represent a new therapeutic strategy to promote healing because induced a significative increase on cell proliferation (while high and low molecular weight-HA have no effect on cell proliferation)
Bibliography:
Prosdocimi Bevilacqua. "Exogenous hyaluronic acid and wound healing: an updated vision". PANMINERVA MED 2012;54:129-35
Ghazi K, Deng-Pichon U, Warnet J-M, Rat P (2012) Hyaluronan Fragments Improve Wound Healing on In Vitro Cutaneous Model through P2X7 Purinoreceptor Basal Activation: Role of Molecular Weight. PLoS ONE 7(11): e48351.
Since 1963, Fidia has pioneered the clinical application of hyaluronic acid and has paved the way to a new concept and a novel medical approach: Regenerative Medicine.
Today, Regenerative Medicine, more specifically Autologous Biological Therapy, offers a promising new synergic role for hyaluronic acid, thanks to the development of new therapeutic strategies in all areas where Fidia is already present, thereby enabling the company to always be a step ahead and establish new standards in medical treatment.

Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is an endogenous therapeutic technology that is gaining interest in regenerative medicine due to its potential to stimulate and accelerate tissue healing.
PRP is defined as an autologous biological product derived from the patient’s blood, and in which after a centrifugation process a plasma fraction is obtained with a platelet concentration higher than that in circulating blood.
Platelets play a crucial role in the wound healing process thanks to their hemostatic function and presence of cytokines and growth factors. The use of growth factors to promote cutaneous wound healing has existed since many decades, and they can be applied in a wide range of ways, either by traditional topical or intralesional administration or by using specific scaffolds.

Stem cell therapy has found widespread use in wound healing, whether acute or chronic.
Nowadays, many cells are studied for wound healing; some of them are stem cells (Adipose derived stem cells (ADSCc), Bone marrow (BM) stem cells), and others are living cells (Monocytes, Leukocytes..)
Adipose tissue is a rich source of cells with emerging promise for regenerative medicine. ADSCs becomes popular because they are readily available in large quantities with minimal morbidity and discomfort associated with their harvest. These cells are contained in the vascular stromal fraction (SVF) of the lipoaspirate when they are separated from the remaining cellular parts (adypocites).
Recent research has largely focused on the signaling properties of ADSCs, particularly related to the release of cytokines and modulation of inflammation. The heterogeneous nature of SVF provides properties of immunomodulation, controlled inflammation, angiogenesis, differentiation and extracellular matrix production to promote regeneration.
In the last decade, these characteristics have made ADSCs the ideal cell for use in wound healing.

© Fidia Farmaceutici S.p.A.
Via Ponte della Fabbrica 3/A - 35031 Abano Terme (PD) - Italy
Tel. (+39) 049 8232221 - 2222 Fax (+39) 049 810653
Cap. Soc. € 36.120.000 int. vers. - C.C.I.A.A. PD n. 80793 - Iscr. Reg. Imp. PD
Cod. Fisc. e P. IVA 00204260285

